Membrane Filters
Sartorius' Broad Range of Membrane Filtration Products Offers Highly Individualized Solutions
Membrane filtration is one of the most effective separation processes and is steadily under development leading to new prospects. Sartorius membranes are available in a wide variety of pore sizes, structures and surface properties to serve nearly unlimited selectivity of separation.
Shop Sartorius Membrane Filters by Type
Membrane Filters Quick Selection Guide
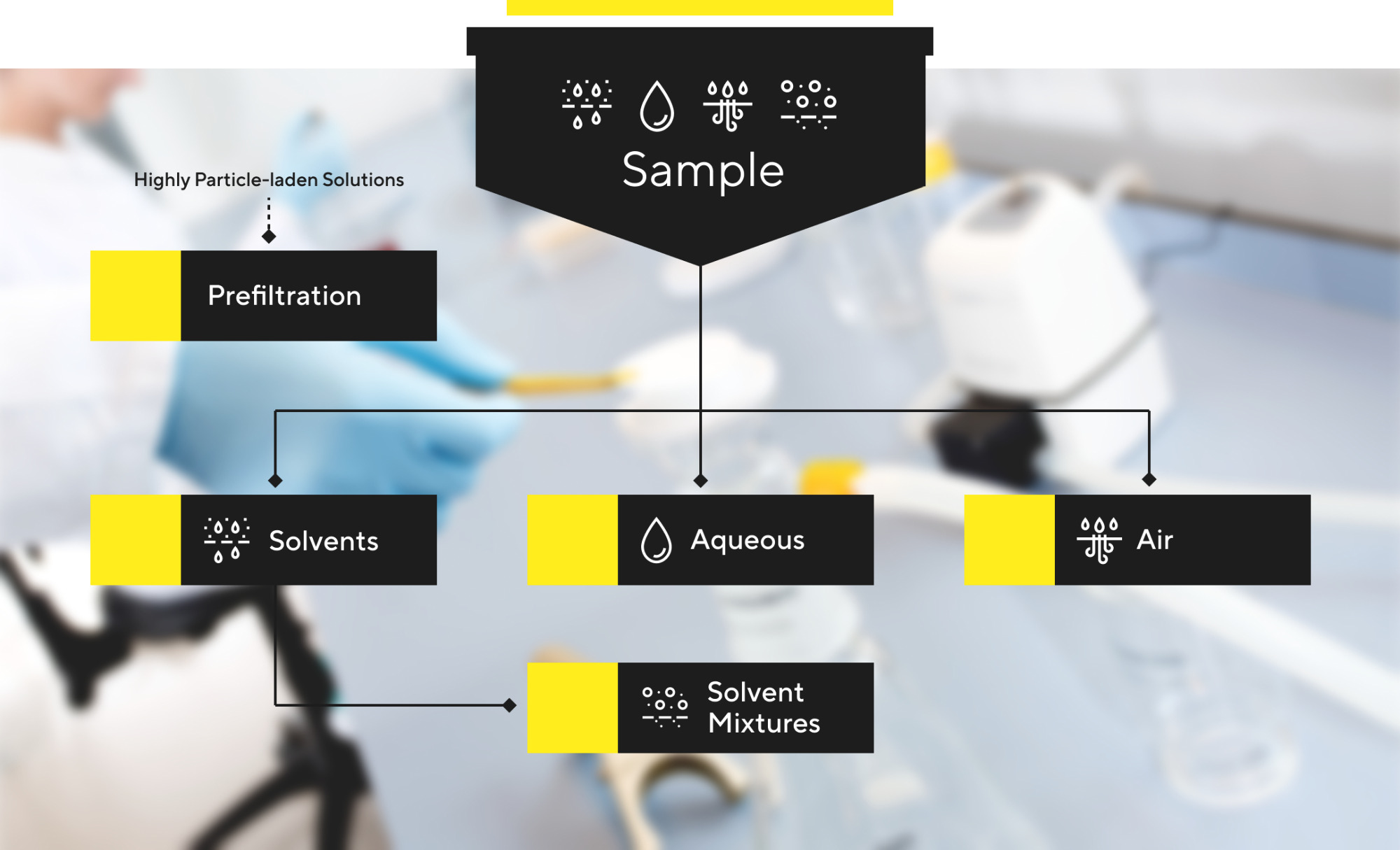
Find Membrane Filters for your Specific Needs
Why Choose Sartorius Membrane Filters?
Sartorius Membrane Features
As the production of membranes mark one of Sartorius’ main competencies, we are proud to offer high expertise and forward our knowledge to you as a customer.
We are covering many essential applications in the life science industry. These include HPLC filtration, bioburden reduction, protein filtration, microbiological testing and many more.
Our product range contains up to seven membrane types and 10 pore sizes. Furthermore, we offer a diameter range from 13mm to 293mm. This allows you to get a membrane that fits your laboratory demands.
Customer Reviews
Membrane Filter Resources & Documentation
Product Documentation
Minimizing TOC with the Right Flush Volume for Membrane Filter Discs
PDF | 525.6 KBFAQs
Membrane Filter Frequently Asked Questions
In case you are not able to find a membrane according to your specific needs, please feel free to reach out to LabFiltrationPM@sartorius.com.
The shelf life of Sartorius membranes are as follows:
Sartorius Stedim Biotech Material name | As manufactured flat filter disc products (years) |
|---|---|
Cellulose Acetate | 5 |
Cellulose Nitrate | 4 |
Reg. Cellulose | 5 |
Ultrafilters | 3 |
Polyamide | 4 |
PESU (Polyethersulfone) | 5 |
Sartobind (Type Q + S) | 5 |
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | 5 |
PC (Polycarbonate) | 5 |
Polymer | Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
Cellulose acetate (CA) |
|
|
Cellulose nitrate |
|
|
Regenerated cellulose (RC) |
|
|
Polyamide (PA) |
|
|
Polyethersulfone (PES) | Low content of extractables |
|
Hydrophobic PTFE | Permanently hydrophobic membranes |
|
Hydrophilic membrane filters have a polar group on the membrane surface which makes them capable of filtering water. In contrast, hydrophobic membranes are unpolar and reject water from passing through. Hydrophobic filters are typically used for air and gas filtration purposes.
Microfiltration is a membrane technical filtration process which retains or removes contaminants in the range from 0.1 µm to 10 µm form fluids (liquid and gas) by passing through a microporous membrane.
- Pressure differential across the membrane
- Filter type
- Filter surface area
- Viscosity of fluid
- Temperature of fluid
- Use of a prefilter
The first step is to ensure that you have the right equipment to perform sterile filtration. This usually includes a membrane filter that can retain bacteria to a certain degree, a filter holder, sterile containers, and the liquid to be filtered. Be sure to sterilize the filter holder and membrane by autoclaving, sterilizing with γ-irradiation, sterilizing with dry heat, or using another sterilization method. Cellulose acetate, cellulose nitrate, polyamide and polyethersulfone membranes with a pore size of 0.22 µm are classified as sterile filters as they have a bacteria retention rate per filter area of 10⁷/cm² with Brevundimonas diminuta. In addition, polyamide and polyethersulfone retain 10⁷/cm² of Serratia marcescens for our 0.45 µm disc filters.
After filtration, collect the filtered liquid in a sterile container and make sure the container is sealed to maintain sterility.
This depends on many factors. You may already know what you want to filter out/retain on the membrane surface (e.g. bacteria, particles, proteins, or something else). Next, you need to choose from a variety of pore sizes, materials, diameters, and specifications.
Materials: Are you looking for a hydrophilic (cellulose acetate/nitrate, polyethersulfone, polyamide, regenerated cellulose) or hydrophobic (polytetrafluorethylene) membrane? Do you need to filter solvents, solvent mixtures, aqueous solutions or air? What type of chemicals are you working with and is compatibility important?
Pore size: Do you need to retain something for further analysis or just remove particles and clean your solution? Choose pores that are smaller than the medium you need to retain. We offer pore sizes from 0.2 µm to a maximum of 8 µm.
Diameter: Choose a filter size that can handle the volume of liquid you need to process. We offer membranes from 13mm - 293mm.
Specifications: What features need to be considered for your operation? Choose from performance characteristics such as flow rate, thickness, thermal resistance, bubble point, etc. to find your optimal membrane solution.
We are happy to assist you in finding the best membrane solution for your laboratory.